- contact@laparoscopyadvice.com
- General Practice Hospital, G-9/2 Islamabad
- Mon - Fri: 10:00 am - 7:00 pm
Visiting Hours
| Mon - Fri: | 8:00 am - 8:00 pm |
| Saturday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
| Sunday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
Gallery Posts






| Mon - Fri: | 8:00 am - 8:00 pm |
| Saturday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
| Sunday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |






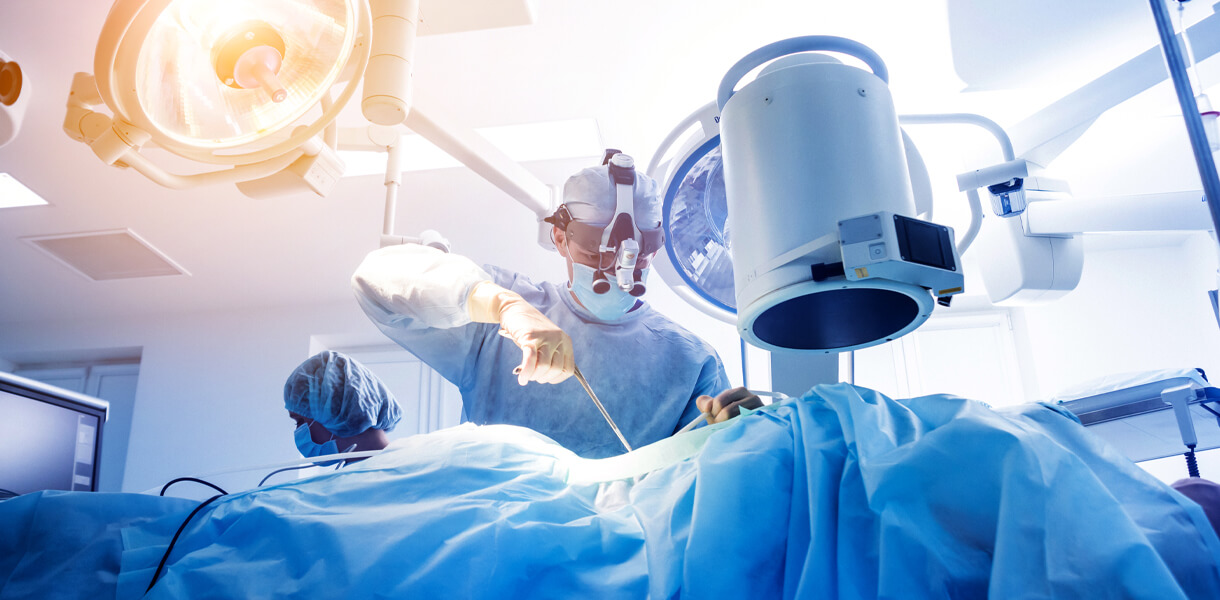
A core needle biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure used to obtain a sample of tissue from a suspicious area for further examination. It is commonly performed to diagnose various conditions, including tumors, infections, and inflammatory diseases, by analyzing the cellular composition and characteristics of the tissue. Core needle biopsy offers several advantages over traditional surgical biopsy, including less scarring, reduced risk of complications, and faster recovery times.
During a core needle biopsy, a specially designed needle with a hollow core is inserted into the target tissue under imaging guidance, such as ultrasound or MRI, to ensure accurate placement. The needle is then advanced into the area of interest, and a cylindrical core of tissue is extracted using a spring-loaded mechanism or manual suction. The collected tissue sample is sent to a pathology laboratory for analysis, where it is processed, stained, and examined by a pathologist under a microscope.
Core needle biopsy may be recommended when other diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or fine-needle aspiration, are inconclusive or inadequate for obtaining a definitive diagnosis. The decision to perform a biopsy is based on various factors, including the size, location, and characteristics of the lesion, as well as the patient’s medical history and symptoms. While core needle biopsy is generally safe, potential risks and complications are rare and can usually be managed with proper technique and post-procedure care.
The signs and symptoms that prompt the need for a core needle biopsy vary depending on the underlying condition or suspected diagnosis. Common indications for biopsy may include:



Q: Can heartburn or acid reflux lead to esophageal cancer?A: Chronic heartburn or acid reflux can contribute to the development of esophageal cancer, particularly adenocarcinoma. Managing acid reflux is crucial for esophageal health.
Q: Are there specific foods to avoid with esophageal cancer? A: Individuals with esophageal cancer may benefit from avoiding spicy, acidic, or rough-textured foods that can irritate the esophagus. Dietary adjustments should be personalized based on individual needs.
Q: Is esophageal cancer hereditary? A: While most cases of esophageal cancer are not directly inherited, there can be a genetic predisposition in some cases. Family history may influence the risk.
| Mon - Fri: | 9:00 am - 7:00 pm |
| Saturday - Sunday: | Off |
Copyright 2023 Adil's Laparoscopy World | Powered by Dynaamx