- contact@laparoscopyadvice.com
- General Practice Hospital, G-9/2 Islamabad
- Mon - Fri: 10:00 am - 7:00 pm
Visiting Hours
| Mon - Fri: | 8:00 am - 8:00 pm |
| Saturday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
| Sunday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
Gallery Posts






| Mon - Fri: | 8:00 am - 8:00 pm |
| Saturday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |
| Sunday: | 9:00 am - 6:00 pm |






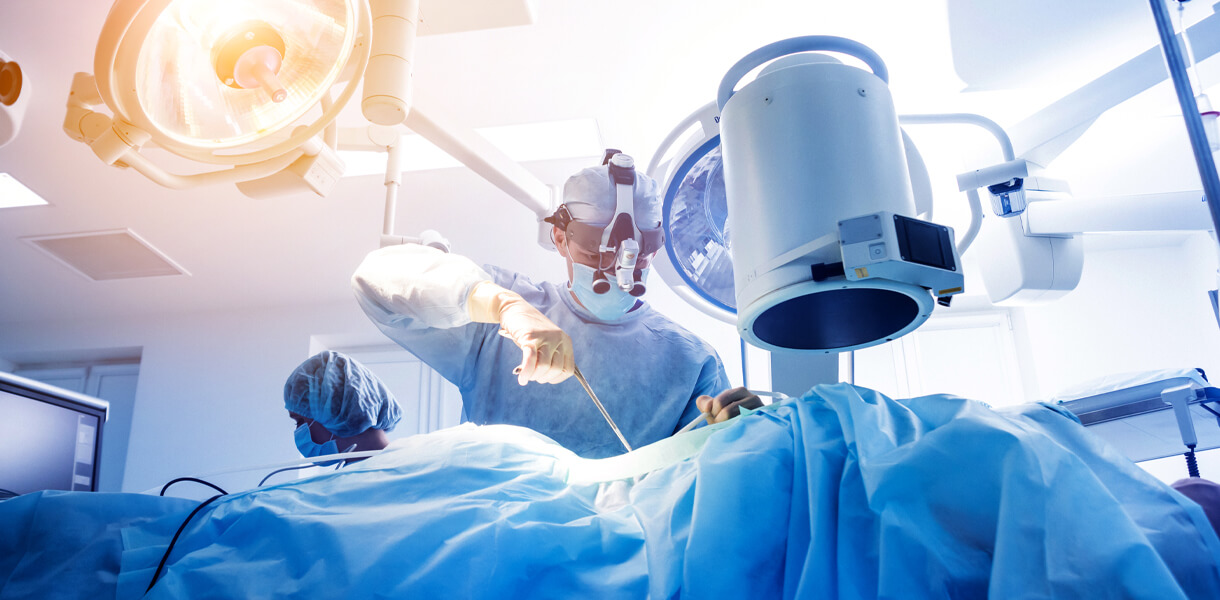
Undescended testes, also known as cryptorchidism, is a congenital condition where one or both testes fail to descend into the scrotum during fetal development. This condition requires medical evaluation and intervention to prevent potential complications and ensure proper testicular function.
During fetal development, the testes form within the abdomen and gradually descend into the scrotum before birth. In cases of undescended testes, one or both testes remain in the abdomen or fail to fully descend into the scrotum. This condition may resolve spontaneously in some infants within the first few months of life, but if the testes remain undescended beyond infancy, medical intervention is necessary.
Unilateral or Bilateral: Undescended testes may affect one or both testes, with unilateral cases being more common.
Palpable or Non-Palpable: The undescended testicle may be palpable within the inguinal canal or abdomen during physical examination, or it may be non-palpable if located deeper within the abdomen.
Hormonal Factors: Disruptions in hormonal signaling during fetal development can affect the descent of the testes into the scrotum.
Genetic Factors: Undescended testes may occur more frequently in infants with a family history of the condition or other congenital abnormalities.
Absence of Testes in Scrotum: The primary sign of undescended testes is the absence of one or both testes in the scrotum at birth or during physical examination.
Palpable Mass: In cases where the undescended testicle is palpable, a firm, non-tender mass may be felt in the groin or lower abdomen.



Hormonal Therapy: In some cases, hormonal therapy with human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) may be used to stimulate testicular descent in infants with undescended testes.
Orchiopexy Surgery: Orchiopexy is a surgical procedure performed to bring the undescended testicle into the scrotum and secure it in place. This procedure is typically recommended between 6 to 12 months of age to optimize testicular function and reduce the risk of complications.
| Mon - Fri: | 9:00 am - 7:00 pm |
| Saturday - Sunday: | Off |
Copyright 2023 Adil's Laparoscopy World | Powered by Dynaamx